Office Hours
Monday – Friday
8:00 AM – 4:30 PM
Phone: (+84) 272 376 9216
Hotline: 0981 152 153
Email: info@ttu.edu.vn
TAN TAO UNIVERSITY
Tan Tao University Avenue, Tan Duc E.City, Duc Hoa, Long An Province
PART I: OVERVIEW OF THE ACADEMIC PROGRAM
- Program Name (in Vietnamese): Ngôn ngữ Anh
- Program Name (in English): English Studies
- Program Code: 7220201
- Degree Awarded: Bachelor
- Program Duration: 4 years
- Degree Title upon Graduation: Bachelor of Arts in English Studies (B.A.)
- Degree-Granting Higher Education Institution: Tan Tao University
- Total Credits: 130
- School: School of Languages
- Medium of Instruction: English
- Website: shl.ttu.edu.vn
- Facebook Page: School of Languages - Tan Tao University
1. General Aims:
The academic program of Tan Tao University (TTU) English studies aims to offer its training to produce high qualified Bachelors who will be proficient in English and use it effectively in academic and non-academic situations, possess well-rounded knowledge about the language and cultures of English-speaking countries, have the ability and cultural knowledge to live, work and implement a renovation in a global English-speaking setting and international integration. Additionally, learners will be equipped with the necessary skills to complete Independent English Study Projects, and will be prepared to apply to a post-graduate or Master’s program to further education and become an expert in their field of study.
2. Specific Program Objectives
2.1. Knowledge:
- General Education Knowledge:
PO1: Acquiring knowledge of political theory, law, economics, society, and culture.
PO2: Effectively applying foreign languages and computer software in the field of economics; demonstrating the ability to read and comprehend specialized documents, and communicate fluently with tourists, partners, and colleagues in English to meet job requirements in a globalization.
- Foundational Knowledge:
PO3: Possessing fundamental knowledge of social sciences, humanities, natural sciences, and technology.
- Knowledge of concentration areas:
PO4: Applying knowledge of English language skills and fields to help learners proficiently use English in various situations (e.g., communication, commerce), become English teachers, translators, or work in English-related positions.
PO5: Applying knowledge in planning, organizing, managing, coordinating, and conducting English teaching and translation activities as well as using business English in enterprises.
2.2. Skills
- Hard Skills
PO6: Demonstrating the English proficiency at level 5 and a second foreign language (Chinese/Korean/Japanese) proficiency at level 3, based on the Vietnamese Foreign Language Proficiency Framework.
- Soft Skills
PO7: Developing soft skills related to working independently and in teams, self-learning, management, and leadership abilities.
PO8: Demonstrating skills in reasoning, critical thinking, and problem-solving, along with the capacity for lifelong self-learning and research to work effectively, as well as creativity and the ability to lead and drive change in professions related to English studies.
2.3. Attitude
PO9: Exhibiting a sense of responsibility and ambition for the trained profession.
PO10: Guiding and supervising others in performing defined tasks, with accountability for personal and group responsibilities.
2.4. Professional Ethics
PO11: Upholding ethical standards, professional conscience, discipline, an industrial work style, and excellent service attitude.
PO12: Possessing political qualities, a sense of professional development, civic responsibility, community accountability, and good health to meet the demands of national development and defense.
| PLOs | Description |
| 3.1. Knowledge | |
| PLO1 | Mastering theoretical and practical knowledge of English studies throughout the breadth and depth of the language in order to use English proficiently in all situations. |
| PLO2 | Applying fundamental knowledge of social sciences, humanities, political science, Vietnamese law, and the liberal arts education of English studies. |
| PLO3 | Using information and communications technology (ICT) to meet job requirements that are related to English studies. |
| PLO4 | Being able to plan, organize, and supervise the application of knowledge in culture and literature, translation and interpretation, and ESL teaching activities. |
| PLO5 | Applying basic knowledge of management and operation of English-related activities. |
| 3.2. Skills | |
| PLO6 | Obtaining skills in analysis, synthesis, evaluation, and others in order to handle complex English-related issues. |
| PLO7 | Being skillful in taking initiative, exercising leadership, and being able to start an English-related business to create jobs for themselves and for other people. |
| PLO8 | Having the ability to evaluate the quality and effectiveness of the English-related tasks assigned, and to appraise other people’s competence to complete their respective work. |
| PLO9 | Assessing the quality and effectiveness of tasks or assignments related to the English language field upon completion, as well as evaluating the performance of individual team members. |
| PLO10 | Communicating (in writing, orally, etc.) with colleagues and
other people in the workplace clearly and effectively, and solving English-related interpersonal challenges. |
| PLO11 | Being able to use another foreign language (Korean, Chinese, Japanese, French, Vietnamese for foreign learners, etc.) at level 3/6 according to the six-level Foreign Language Proficiency Framework for Vietnam. |
| 3.3. Automony and Responsibility | |
| PLO12 | Demonstrating the capacity to work independently, develop self-learning and research skills, and engage in both online and offline learning; commiting to lifelong learning to ensure sustainable employability, and working effectively in teams, with accountability for personal and group responsibilities. |
| PLO13 | Guiding and supervising others in performing specific tasks and professional duties. |
| PLO14 | Self-directing, drawing professional conclusions, and defending personal viewpoints, adapting to, and implementing creative solutions, including initiating or participating in entrepreneurship projects related to the English language. |
| PLO15 | Planning, organizing, managing, and coordinating professional tasks involving resource utilization in the workplace; evaluating task performance and proposing solutions to improve outcomes. |
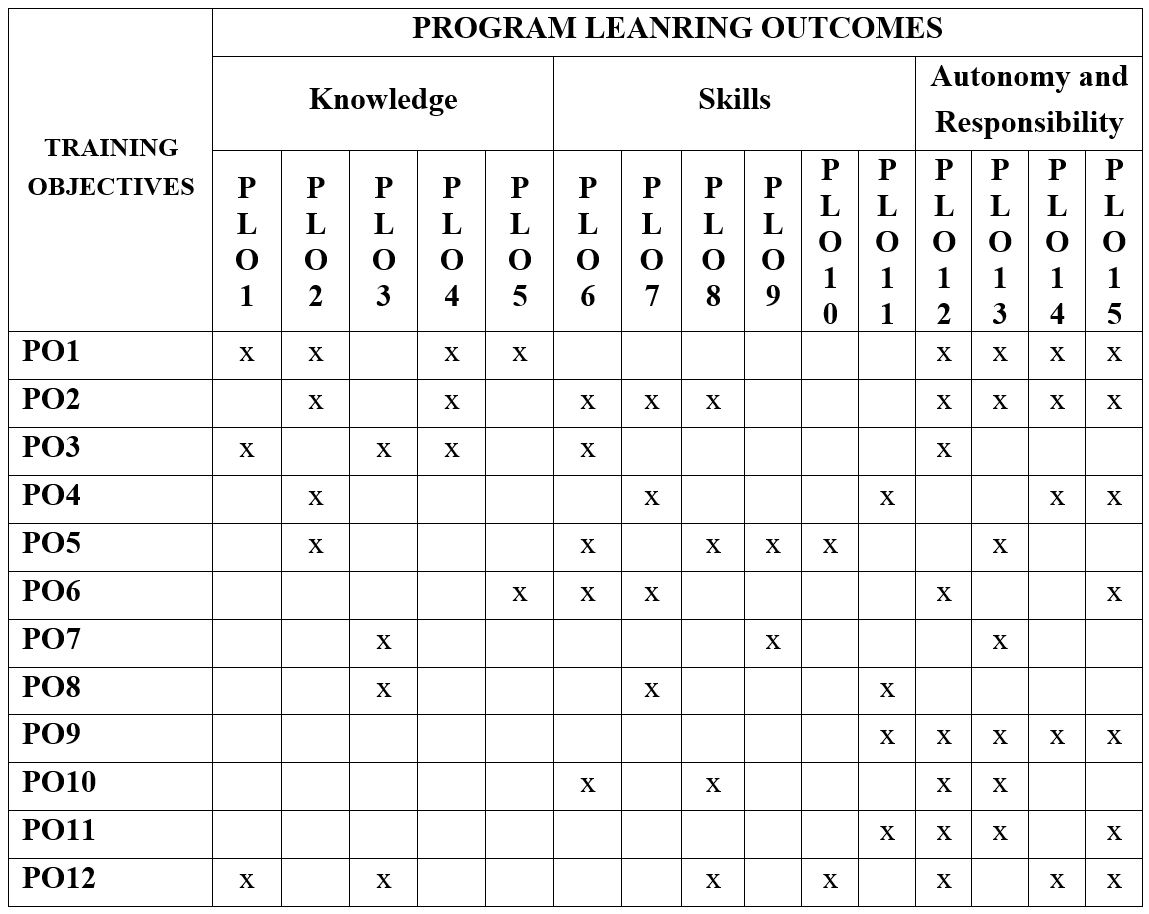
Table 1. Matrix integrating the Program's Objectives and Learning Outcomes
Graduates of the English Studies program at Tan Tao University can pursue various career paths, including but not limited to:
- Teaching general English at public and private schools, teaching business English at various institutions, language centers, or starting English entrepreneurial projects
- Working as translators and interpreters in government agencies, publishing houses, notary offices, news agencies, media companies, or human resource departments.
- Workign as specialists in commerce and import-export at trading companies, financial corporations, banks, domestic and international companies using English
- Being secretaries or foreign affairs assistants in companies, enterprises, economic corporations, consulates, non-governmental organizations, or diplomatic agencies.
- Workign as cultural officers or tour guides.
- Pursuing Master's degrees at international universities either in Vietnam or abroad.
Attainment level with job positions:
(Level achieved: 1: Ability to know; 2: Ability to understand and apply; 3: Ability to analyze and evaluate; 4: Ability to create)
| No. | JOB POSITIONS | Attainment level | |||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||
| 1 | English teacher | X | |||
| 2 | Translator | X | |||
| 3 | Interpreter | X | |||
| 4 | Office staff | X | |||
| 5 | Editor | X | |||
| 6 | Human Resources Staff | X | |||
| 7 | Study-Abroad Consultant | X | |||
| 8 | Secretary/Assistant (School, Department, Company, Organization) | X | |||
| 9 | Employees for foreign companies; non-governmental organization (NGO) | X | |||
| 10 | Cultural Officer; Tour guide | X | |||
| 11 | As a Master's student at a university at home and abroad | X | |||
- Graduates will have the ability to engage in self-learning, research, and exploration in their work environment to enhance their professional knowledge and skills. They will also develop organizational capabilities for professional activities, meeting the demands of the country’s industrialization and modernization process.
- They will possess the capacity to pursue higher levels of education to further their knowledge and professional skills, catering to both personal and societal needs.
Graduates with a Bachelor's degree in English Studies can work in various roles and positions, including: Teaching at public elementary schools, secondary schools, and high schools (with an additional TESOL certificate) or private institutions; working at language centers, publishing houses, translation offices, travel agencies, or companies and enterprises where English is used; or employment at higher education institutions or vocational education centers (after pursuing further qualifications).
1. Admissions Information
All candidates must meet the requirements outlined in the Ministry of Education and Training’s regulations for university admissions.
2. Training Process
- The academic program is governed by credit-based regulations, enabling students to actively and proactively adapt to the learning process for optimal academic and personal development outcomes.
- The program is designed to span 8 semesters (equating 4 academic years), with a total of 130 credits. The official duration of study is 4 years, with a minimum of 4 years and a maximum of 8 years for program completion.
Each academic year is divided into 2 main semesters, including Fall and Spring. Additionally, the Provost may approve a summer semester to allow students to retake courses, improve their grades, or advance their studies.
Each main semester includes 12-15 weeks of instruction (depending on the number of class hours per week) and 3 weeks for exams.
Each summer semester includes at least 6 weeks of instruction and 1 week for exams.
In accordance with the Undergraduate Training Regulations of (Issued together with Decision No.31/QĐ-TTU.21 dated June 30, 2021 by Provost of Tan Tao University). Learners will be evaluated and granted graduation status if they meet the following conditions:
- Accumulating all required courses, credits, and complete other mandatory components as stipulated by the training program;
- Successfully completing at least one concentration area within the list of concentration areas offered;
- Achieving a minimum cumulative GPA of 2.00 for the entire program.;
- Meeting the university's English proficiency requirements for graduation, including a TOEFL score of 600, IELTS 7.0, or equivalent (refer to the equivalency conversion chart for various exams), and achieving a second foreign language (Chinese/Korean/Japanese) proficiency equivalent to Level 3/6 on the Vietnamese Foreign Language Proficiency Framework.;
- Completing the required courses in Physical Education (PE) and National Defense and Security Education (NDSE)
- Obtaining a Soft Skills Certificate issued by Tan Tao University;
- Fulfilling the required number of hours for community service activities as prescribed;
-Demonstrating “Good Academic and Disciplinary Standing”, not under investigations.
- Completing all obligations to the university.
- Submitting a graduation application following the guidelines provided by the Training Management Office.
Teaching and learning activities in the training program are designed to ensure learners' comprehensive development in knowledge, skills, and attitudes. A variety of methods are applied to help learners achieve the program's expected learning outcomes. The teaching strategies are categorized into nine main groups: direct teaching, experiential learning, art-based teaching, critical thinking, interactive learning, research-oriented teaching, technology-based teaching, and self-directed learning.
1. Direct Teaching
Direct teaching is a method in which information is delivered directly to learners, with the instructor presenting and learners listening. This method is commonly used in traditional classrooms and is effective for imparting basic information or explaining new skills. The specific methods under this strategy include: explicit explanation, lecture, seminar, open-ended questioning, and simulation.
Explicit Explanation (TLM1): This method involves instructors providing detailed explanations and specific guidance on lesson content, helping students achieve both knowledge and skills-related objectives.
Lecturing (TLM2): The instructor presents and explains the lesson content. Students listen, take notes, and acquire the knowledge delivered. Interactive or segmented lectures may be used to actively engage learners.
Seminar (TLM3): Learners participate in sessions where guest speakers from relevant fields (e.g., experienced educators or professionals) share knowledge and expertise to provide learners with broad or specific insights into their field of study.
Open-ended Questioning (TLM4): During lessons, the instructor uses open-ended questions or scenarios to guide students in gradually forming answers. Group discussions may be employed to collaboratively solve problems or complete exercises.
2. Experiential Learning
Experiential learning methods focus on encouraging learners to practice and engage in real-world scenarios. This promotes exploration, problem-solving, and interaction with others. The methods include games, practice, internships/fieldwork, debates, discussions, modeling, and community service learning.
Activity-based learning is also known as project-based learning (this method facilitates independent and collaborative learning). Learners progress through activities at their own pace and interests while they take responsibility for their own learning and gain lifelong collaboration and negotiation skills.
Games (TLM5): Games involve challenges, competitions, or collaborations under clear rules. They provide opportunities for learners to enhance practical knowledge, decision-making, communication skills, and teamwork.
Practice (TLM6): This method involves learners observing instructor demonstrations and independently completing tasks under guidance to develop specialized skills for future careers.
Debate (TLM7): Instructors present issues related to lesson content, and learners with opposing views analyze and defend their perspectives to persuade others. This helps develop critical thinking, negotiation, public speaking, and decision-making skills.
Group Discussion (TLM8) Learners, divided into small groups (6–10 members), discuss issues raised by the instructor. Unlike debates, discussions involve participants with aligned views collaborating to refine and complete their solutions. Unlike debate, in the discussion method, learners with the same view of the common goal find evidence to supplement and complete their views and solutions. Topics often used in teaching and learning with group discussions include: problems, proposed solutions, the most suitable solution to content, situation, and cultural aspects, and others.
Internships (TLM9): Through activities at educational institutions, foreign companies (especially those located in two Industrial Parks: Tan Duc Industrial Park, Duc Hoa District, Long An and Tan Tao Industrial Park, Binh Tan District), or language centers, learners gain practical experience in their field of study, form skills, and explore career opportunities.
3. Art-Based Teaching
Art-based teaching helps learners develop intellectually, creatively, socially, emotionally, and physically. Common methods include:
Role-Playing (TLM10): This method simulates real-life scenarios and emphasizes communication skills, allowing students to assess knowledge and solve problems in specific contexts.
Performing (TLM11): Activities such as acting, storytelling, and dramatizations engage learners in script reading, role-playing, costume creation, and collaborative performance, fostering teamwork and cognitive development.
4. Critical Thinking
Teaching critical thinking involves methods aimed at developing critical thinking, questioning skills, analytical skills, and reflective practices in learners' approaches to learning. These methods are also designed to promote creative and independent thinking and learning for students. The methods applied in teaching critical thinking include:
Problem-Based Teaching (TLM12): This educational approach places students at the center of the learning process. Problems used in teaching and learning are carefully constructed with appropriate structures so that, through the process of finding solutions to the given problem, students acquire the knowledge and skills required by the course.
Case-Study Learning (TLM13): This learner-centered teaching method helps students develop analytical, critical thinking, and communication skills. In this method, instructors design tasks based on real-life situations, problems, or challenges in the workplace, requiring students to solve them. Through this process, students develop problem-solving skills, decision-making abilities, and research competencies.
Brainstorming (TLM14): This method involves group work to generate solutions or ideas around a particular topic. Each group member is encouraged to contribute ideas without concern for feasibility, fostering flexible thinking and enhancing the ability to identify and solve problems. It also stimulates the development of creative thinking and information-seeking skills. The technique involves dividing the class into small groups of 4–5 members with an experienced and objective facilitator who can pose questions, lead conversation and motivate creativity.
Mind-Mapping (TLM15): This method addresses problem-solving through visual representation in the form of a map or diagram. Mind maps are designed based on logical thinking and can be represented as a wheel-spoke model, a roadmap, or a tree structure. Learners identify keywords and related issues and may use font sizes, styles, colors, or images to indicate different levels and degrees of information. Mind mapping can be applied for note-taking, summarizing content, planning, preparing presentations, or creatively solving problems.
5. Research-Oriented Teaching
Research-oriented teaching fosters a high level of critical thinking. Learners identify research questions, find suitable methods to solve problems, or report conclusions based on evidence collected using methods such as independent research, project-based research, research-teaching groups, and academic support activities.
Independent Research (TLM16): This method develops students' ability to plan, explore, organize, and communicate a topic independently and in detail under the guidance of an instructor. It also enhances learning motivation and active engagement, as students are allowed to choose the materials they wish to present.
Project-Based Research (TLM17): Learners research a topic related to the course and write a report.
Research-Oriented Teaching (TLM18): Learners are encouraged to participate in instructors’ research projects or teaching groups, helping them develop research competencies and creative skills. This serves as a foundation for further academic pursuits at the postgraduate level.
Teaching Assistantship ad Academic Support (TLM19): Learners assist instructors in teaching-related tasks in the classroom.
6. Technology-Based Teaching (TLM20):
Technology-based teaching plays a crucial role in modern education. Programs should widely adopt online learning methods (e-learning) where instructors and learners utilize digital tools to facilitate teaching and learning.
7. Self-Directed Learning
Self-directed learning is a method that helps learners acquire knowledge and develop skills to be self-directed, proactive and independent in learning. Learners have the opportunity to choose a topic to study, explore and research a problem in depth. From there, learners develop time management skills and self-monitor their learning. The self-directed leanring method is mainly applied for homework assignments.
Assignment Assessment (TLM21): Learners are assigned tasks to work at home with content and requirements set by the instructor. Through completing these assigned tasks, learners learn how to self-study, as well as gain the required knowledge and skills.
- Studying the learning outcomes of each assigned course;
- Reviewing the knowledge and skill requirements of the course and compare them with the framework curriculum;
- Researching materials and textbooks for the courses;
- Developing a course syllabus aligned with the course’s learning outcomes and the program’s overall learning outcomes;
- Designing course activities that meet the needs of the students.
- The academic program is reviewed every two years to make adjustments that address the needs of students and other stakeholders. Various forms of support are provided to students to foster ethical values, professionalism, and skills.
- Annually, the School makes plans for observing classes, especially those taught by young and new instructors, to share knowledge, teaching methods, and enhance instructors’ capabilities.
- Feedback from students regarding instructors' qualities, expertise, ethics, and professionalism is regularly collected.
- The School frequently seeks input from stakeholders regarding the demand for graduates in the job market.
1. Assessment Methods
The assessment methods employed in the training program are categorized into two main types: formative evaluation and summative evaluation. The specific formats and contents of these evaluations are outlined in the university's current training regulations and detailed in the course syllabus of each module.
1.1. Formative Assessment
The purpose of formative evaluation is to provide timely feedback from instructors and learners regarding progress and areas for improvement throughout the teaching and learning process.
Specific methods of formative evaluation adopted by the university include attendance, regular assessments, and mid-term evaluations. The following methods may be utilized to assess learners in 1-2 credit modules: attendance evaluation, assignment evaluation, group work, presentations, and multiple-choice tests. For 3-5 credit modules, in addition to these methods, some summative evaluation methods (listed in 12.1.2) may also be used for mid-term evaluations.
Attendance Assessment (AM1): This method reflects the learner's study attitude through regular participation in class sessions and self-study hours. Active participation helps learners systematically acquire knowledge, develop skills, and form proper attitudes and good behaviors. Attendance evaluation is carried out using rubrics tailored to the nature of individual courses.
Assignment Assessment (AM2): Learners are required to complete tasks related to the lesson during or after class, either individually or in small groups. These tasks are assessed based on specific criteria (assignment rubric).
Presentation Assessment (AM3): In some courses, learners work in groups to solve problems or discuss topics related to the lessons, presenting their findings to other groups. This activity not only enhances subject knowledge but also develops communication, negotiation, and teamwork skills. Achievement in these areas is assessed using specific rubrics (presentation rubric).
1.2. Summative Assessment (End-of-Term)
The goal of summative assessment is to make conclusions about the achievement of learning objectives, assess learning outcomes, and rank the progress of learners at specific period of time during the program, such as the end of a term or the completion of a course.
Assessment methods used include written, multiple-choice, and oral exams, presentations, group work, practical assessments, and final projects. (The university employs the following summative evaluation methods, which may also be used for mid-term assessments in 3-credit modules)
Written Tests (AM4): Under this assessment method, learners are required to answer a number of questions, case studies, or provide personal opinions on issues related to the course's learning outcomes. The assessment is based on pre-determined answer keys. A 10-point scale is used for grading. The number of questions in the assessment is determined by the specific knowledge requirements of the course.
Multiple Choice Tests (AM5): Similar to written tests, this method evaluates learners' knowledge using pre-designed answer options, where learners select the correct answers.
Oral Exams (AM6): Learners are assessed through direct interviews or Q&A sessions. Criteria for assessment are outlined in specific rubrics (oral exam rubric).
Report Writing (AM7): Learners are assessed based on the quality of their written reports, including the content, explanatory details, illustrations, and diagrams. Assessment criteria are specified in report rubrics for each course.
Presentation (AM8): This method reflects the presentation evaluation described in formative evaluation but is conducted periodically at mid-term, end-of-term, or program completion.
Group Work Assessment (AM9): This method assesses learners' teamwork skills, such as organizing, managing, building effective teams, leading group activities, and developing team dynamics. Assessment is based on specific group work rubrics.
Internship Report/Thesis (AM10): This is a highly valuable assessment method because it evaluates knowledge, attitude, and various skills (including creative thinking, judgment, reasoning, information retrieval, organizational management, communication, collaboration, data processing, and report writing). Learners are assessed by their academic advisors, workplace mentors, or a thesis evaluation committee using appropriate evaluation forms tailored to the program's requirements.
2. Assessment Form, Weight, and Criteria
According to the training regulations of Tan Tao University.
Based on the regulations of the Department, details are shown in the course syllabuses.
3. Assessment Scale
According to the training regulations of Tan Tao University.
1. Graduation Thesis
1.1. Conditions for Writing a Graduation Thesis:
- Students must have accumulated all required courses in the curriculum at the time of review.
- The cumulative GPA must meet the Tan Tao University's requirements.
- Students in their final academic year must not be under criminal investigation.
- Students must have a qualified instructor (including instructors from another university) who agrees to supervise them, and the approval of the Faculty Board is required.
The number of students eligible to write a graduation thesis must not exceed 50% of the total number of students in each training program during the review period. For specialized fields, the School of Languages may submit specific cases for review by the University Board.
Depending on the number of instructors who register to supervise thesis topics and the availability of facilities, the School will propose the number of students permitted to write a thesis for the Provost’s approval. The University encourages students to write a graduation project or thesis and find their own supervisors if the number of topics registered by instructors is insufficient, provided the School grants permission.
1.2 Topics for Graduation Thesis
- Students may select one topic related to English Studies that aligns with their career aspirations after graduation. The list of topics will be determined by the Provost based on the resources and available supervisors in the School.
- The grade for the graduation thesis will be included in the cumulative GPA of the entire academic program.
- The graduation thesis is assessed in accordance with the regulations of the Ministry of Education and Training and the specific guidelines of the Tan tao University's assessment forms.
2. Accumulation of Graduation Knowledge
- Target Audience: Students who opt to write essays and complete additional courses (as an alternative to writing a graduation thesis).
- Students will write an essay on a topic related to English Studies or the English language (under the supervision of an instructor) that meets the required criteria (without defending it before an evaluation committee) and complete two substitute courses. The total credits of the substitute courses will be equivalent to the 8 credits of a graduation thesis.
- The grades of the substitute courses will be included in the cumulative GPA of the program.
1. Teaching Staff
- Instructors for the English Studies program must meet the requirements set forth by the Ministry of Education and Training.
- The teaching staff includes both Vietnamese and international instructors.
- Theoretical courses must be delivered by full-time faculty members.
2. Facilities
- The higher education institution must ensure facilities comply with current regulations and guidelines from the Ministry of Education and Training, including classrooms, libraries, modern teaching equipment to support active learning, and computer labs with internet access.
PART II: TEACHING PROGRAM
The program structure ensures a logical and balanced arrangement for each semester of the academic year and each branch of knowledge. Courses are organized progressively from basic to advanced levels, ensuring a continuous flow of knowledge, gradual complexity, and adequate time for learners to accumulate knowledge, and develop skills, ethics, and attitudes necessary for post-graduation work. Additionally, the program is designed to provide an in-depth focus on specific fields of specialization.
The program content includes blocks of general education, foundational disciplinary knowledge, and specialized knowledge, progressively delivered through courses. At the same time, it helps learners enhance soft skills, computer skills, and foreign language proficiency,… and cultivate discipline, professionalism, and workplace safety habits.
The program structure: The total amount of knowledge to be accumulated for the entire program is 130 credits (excluding credits for physical education and defense-security education) and is distributed as follows:
| No. | Academic Load | Credits | ||
| Total | Theory | Practice | ||
| 1 | General knowledge (including elective liberal education courses but excluding Physical Education and National Defense & Security Education content) | 57 | 57 | 0 |
| - Social and Natural Sciences knowledge | 13 | 13 | 0 | |
| - Foundational knowledge of the major | 20 | 20 | 0 | |
| - General courses of Faculty | 24 | 24 | 0 | |
| 2 | Professional knowledge | 61 | 61 | 0 |
| - Basic knowledge of the major | 37 | 37 | 0 | |
| - Specialized knowledge (including electives) | 24 | 24 | 0 | |
| 3 | Graduation | 12 | 6 | 6 |
| - Graduation exam | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| - Graduation thesis | 8 | 4 | 4 | |
| - Graduation internship | 4 | 2 | 2 | |
| Total: | 130 | 124 | 6 | |
| No. | Code | Courses | Credits | |||
| Total | Hours | Theory | Practice | |||
| GENERAL KNOWLEDGE | 57 | 855 | 57 | 0 | ||
| 1. Social and Natural Sciences knowledge | 13 | 195 | 13 | 0 | ||
| 1 | LAW102 | Fundamentals of law | 2 | 30 | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | MACL104 | Ho Chi Minh’s Thought | 2 | 30 | 2 | 0 |
| 3 | MACL108 | Marxist-Leninist Philosophy | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 4 | MACL109 | Political Economy | 2 | 30 | 2 | 0 |
| 5 | MACL110 | Scientific Socialism | 2 | 30 | 2 | 0 |
| 6 | MACL111 | History of the Communist Party of Vietnam | 2 | 30 | 2 | 0 |
| Physical Education and National Defense & Security Education | ||||||
| 1 | MACL1051 | Physical Education 1* | 1 | 30 | 0 | 1 |
| 2 | MACL1052 | Physical Education 2 | 1 | 30 | 0 | 1 |
| 3 | MACL1053 | Physical education 3 | 1 | 30 | 0 | 1 |
| 4 | MACL106 | National Defense & Security Education | 8 | 150 | 6 | 2 |
| 5 | SSE101 | Soft skills * | 2* | |||
| 6 | Practical Experience - Creative Experience and Community Service * | 120 | ||||
| 2. Basic Sciences: Introduction to Informatics and Liberal Arts (Choose 1 from each group of liberal arts courses) | 20 | 300 | 20 | 0 | ||
| 1 | INF102 | Introduction to Informatics | 2 | 30 | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | Human Civilizations | |||||
| 2.1 | HIS101 | World Civilizations | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 2.2 | HIS102 | Modern times | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 3 | Humans and the Earth | |||||
| 3.1 | ENV101 | Human and Environment | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 3.2 | ENV102 | Climate change | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 4 | Critical thinking and Communications | |||||
| 4.1 | HUM101V | Writing and ideas | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 4.2 | MGT102 | Leadership and Communication | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 4.3 | HUM205 | Language and Vietnamese | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 5 | Culture, Literature and Arts | |||||
| 5.1 | ENGL108 | Introduction to Cultural studies | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 5.2 | ART101 | Contemporary art | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 5.3 | CUL101 | Vietnamese and other typical cultures | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 5.4 | HUM102 | Culture and literature | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 6 | Economics and Management | |||||
| 6.1 | PRFN01 | Personal finance | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 6.2 | ENTR01 | Entrepreneurship | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 7 | Natural science & Technology | |||||
| 7.1 | MATH101V | Calculus 1 | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 7.2 | DSP101 | Introduction to data science with Python | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 7.3 | EGD101 | Thiết kế kỹ thuật
Engineering design |
3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 3. The School’s General Courses | 24 | 360 | 24 | 0 | ||
| 1 | ENGL101 | Listening & Speaking 1 | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| ENGLi101 | Reading & Writing 1 | |||||
| 2 | ENGL102 | Listening & Speaking 2 | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| ENGLi102 | Reading & Writing 2 | |||||
| 3 | ENGL103 | Listening & Speaking 3 | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| ENGLi103 | Reading & Writing 3 | |||||
| 4 | ENGL104 | Listening & Speaking 4 | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| ENGLi104 | Reading & Writing 4 | |||||
| 5 | FL101 (FL101_CH /FL101_KO
/FL101_JP) |
Second foreign language (Chinese 1, Japanese 1, Korean 1) | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 6 | FL102 (FL102_CH
/FL102_KO /FL102_JP) |
Second foreign language (Chinese 2, Japanese 2, Korean 2) | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 7 | FL103 (FL103_CH
/FL103_KO /FL103_JP) |
Second foreign language (Chinese 3, Japanese 3, Korean 3) | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 8 | FL104 (FL104_CH
/FL104_KO /FL104_JP) |
Second foreign language (Chinese 4, Japanese 4, Korean 4) | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| PROFESSIONAL KNOWLEDGE | 61 | 915 | 61 | 0 | ||
| Fundamental knowledge of the major | 37 | 555 | 37 | 0 | ||
| 1 | LING101 | Pronunciation Practice | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 2 | ENGR101 | Grammar in Use | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 3 | ENGL110 | Lexicology | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 4 | ENGL184S | Readings in Genre | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 5 | CUL201 | Cross Cultural Communication | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 6 | COMP201 | Composition | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 7 | LING201 | Introduction to English Linguistics | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 8 | ENGL201 | Syntax | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 9 | ENGL208 | Semantics | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 10 | ENGL251 | American- British Literature | 4 | 60 | 4 | 0 |
| 11 | SLA301 | Second Language Acquisition | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 12 | LING301 | Research Study | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| Elective courses: Choose 02 courses (06 credits) from 07 courses | 6 | 90 | 6 | 0 | ||
| 1 | ENGL206 | Variety in Language | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 2 | ENG221S | Digital writing | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 3 | ENGL305 | Pragmatics | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 4 | INST401 | Independent Study | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 5 | LING415 | Sociolinguistics | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 6 | ESP301 | English for Tourism | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 7 | ESP201 | English for Media and Communications | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| Courses for specializations: 18 credits (Choose 1 of 3 concentrations ) | 18 | 270 | 18 | 0 | ||
| A | Business English | 18 | 270 | 18 | 0 | |
| 1 | BENG301 | Commercial Correspondence and e-Commerce | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 2 | BENG302 | English for Business Communication | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 3 | BENG303 | English for Business Administration | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 4 | BENG304 | Dịch thương mại
Business Translation |
3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 5 | BENG305 | International Business Communication | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 6 | BENG306 | English for Logistics | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| B | Translation-Interpretation | 18 | 270 | 18 | 0 | |
| 1 | LING306 | Introduction to Translation & Interpretation | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 2 | TRAN301 | Translation | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 3 | INTE301 | Interpretation | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 4 | LING427 | Contrastive Analysis | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 5 | TRAN401 | Advanced Translation in Practice | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 6 | INTE401 | Advanced Interpretation in Practice | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| C | Teaching English (TESOL) | 18 | 270 | 18 | 0 | |
| 1 | LING340 | Theories of English teaching | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 2 | LING343 | Teaching activities | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 3 | CALL301 | Computer-assisted language learning (CALL) | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 4 | ENGL306 | Curriculum development | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 5 | ENGL307 | Teaching English to young learners | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 6 | LING343 | Testing and assessment | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| Internship, Graduation Thesis, or Thesis Substitute Course | 12 | 300 | 6 | 6 | ||
| 1 | ENGL396 | Internship | 4 | 120 | 2 | 2 |
| GRAT396 | Graduation thesis | 8 | 180 | 4 | 4 | |
| * Students who do not meet the requirements to complete the graduation thesis will write a research paper (equivalent to 04 credits) and take 02 substitute courses (equivalent to 04 credits) | ||||||
| 1 | GRTE396 | Graduation essay | 4 | 90 | 2 | 2 |
| 2 | ESP202 | English for Human Resources | 2 | 45 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | ENGL401 | English Entrepreneurship | 2 | 45 | 1 | 1 |
| TOTAL CREDITS OF THE TRAINING PROGRAM | 130 | 2070 | 124 | 6 | ||
| Total required credits | 106 | |||||
| Minimum total elective credits | 24 | |||||
| No. | Course Code | Course Names | Credits | |||
| Total | Hours | Theory | Practice | |||
| Semester 1 | ||||||
| 1 | MACL108 | Philosophy of Marxism and Leninism | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 2 | LAW102 | Fundametals of law | 2 | 30 | 2 | 0 |
| 3 | Human Civilizations: Choose 1 from the courses | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 | |
| HIS101 | World Civilizations History | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 | |
| HIS102 | Modern Times | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 | |
| 4 | ENGL101 | Listening & Speaking 1 | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 5 | ENGLi101 | Reading & Writing 1 | ||||
| 6 | MACL1051 | Physical Education 1 | 1* | 30 | 0 | 1 |
| 7 | INF102 | Introduction to Informatics | 2 | 30 | 2 | 0 |
| 8 | LING101 | Pronunciation Practice | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| Total: | 13 | 240 | 16 | 0 | ||
| Semester 2 | ||||||
| 1 | MACL109 | Political Economics of Marxism and Leninism | 2 | 30 | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | MACL110 | Scientific Socialism | 2 | 30 | 2 | 0 |
| 3 | Cultural, Literature, and Arts: Choose 1 from the courses | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 | |
| ENGL108 | Introduction to Cultural Studies | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 | |
| ART101 | Contemporary Art | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 | |
| CUL101 | Vietnamese and Other World Classic Cultures | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 | |
| HUM102 | Culture and Literature | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 | |
| 4 | ENGL102 | Listening & Speaking 2 | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 5 | ENGLi102 | Reading & Writing 2 | ||||
| 6 | MACL1052 | Physical Education 2 | 1* | 30 | 0 | 1 |
| 7 | ENGR101 | Grammar in Use | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 8 | ENGL110 | Lexicology | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| Total: | 16 | 240 | 16 | 0 | ||
| Summer Semester | ||||||
| MACL106 | National Defense and Security Education | 8 | 150 | 6 | 2 | |
| Semester 3 | ||||||
| 1 | MACL104 | Ho Chi Minh’s Thought | 2 | 30 | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | Critical Thinking and Communications: Choose 1 from the courses | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 | |
| HUM101V | Writing and Ideas | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 | |
| MGT102 | Leadership and Communication | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 | |
| VNL101 | Language and Vietnamese | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 | |
| 3 | ENGL103 | Listening & Speaking 3 | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 4 | ENGLi103 | Reading & Writing 3 | ||||
| 5 | MACL1053 | Physical Education 3 | 1* | 30 | 0 | 1 |
| 6 | FL101 | Second Foreign Language (Chinese 1, Japanese 1, Korean 1) | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 7 | ENGL184S | Readings in Genre | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 8 | CUL201 | Cross-cultural Communication | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| Total: | 17 | 255 | 17 | 0 | ||
| Semester 4 | ||||||
| 1 | MACL111 | History of the Communist Party of Vietnam | 2 | 30 | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | ENGL104 | Listening & Speaking 4 | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 3 | ENGLi104 | Reading & Writing 4 | ||||
| 4 | Humans and the Earth: Choose 1 from the courses | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 | |
| ENV101 | Human and Environmental Interactions | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 | |
| ENV102 | Climate Change | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 | |
| 5 | FL102 | Second Foreign Language (Chinese 2, Japanese 2, Korean 2) | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 6 | COMP201 | Composition | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 7 | LING201 | Introduction to Linguistics | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| Total: | 17 | 255 | 17 | 0 | ||
| Semester 5 | ||||||
| Required | 16 | 240 | 16 | 0 | ||
| 1 | Natural Sciences & Technology: Choose 1 from the courses | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 | |
| MATH101V | Calculus 1 | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 | |
| DPS101 | Introduction to Data Science with Python | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 | |
| EGD101 | Engineering Design | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 | |
| 2 | ENGL201 | Syntax | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 3 | ENGL208 | Semantics | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 4 | ENGL251 | British-American Literature | 4 | 60 | 4 | 0 |
| 5 |
FL103 |
Second Foreign Language (Chinese 3, Japanese 3, Korean 3) | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| Elective: Choose 01 from the courses | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 | ||
| 1 | ENGL206 | Variety in Language | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 2 | ENG221S | Digital writing | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 3 | ENGL305 | Pragmatics | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| Total: | 19 | 285 | 19 | 0 | ||
| Semester 6 | ||||||
| Required | 12 | 180 | 12 | 0 | ||
| 1 | Economics and Management: Choose 1 from the courses | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 | |
| ENTR101 | Entrepreneurship | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 | |
| PRFN01 | Personal Finance Management | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 | |
| 2 | SLA301 | Second Language Acquisition | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 3 | LING301 | Research Studies | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 4 | FL104 | Second Foreign Language (Chinese 4, Japanese 4, Korean 4) | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| Elective: Choose 01 from the courses | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 | ||
| 1 | ESP301 | English for Tourism | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 2 | ESP201 | English for Media and Communications | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 3 | INST401 | English Study | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 4 | LING415 | Sociolinguistics | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| Total: | 15 | 225 | 15 | 0 | ||
| Semester 7 (Business English Concentration) | ||||||
| 1 | BENG301 | Commercial Correspondence and e-Commerce | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 2 | BENG302 | English for Business Communication | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 3 | BENG303 | English for Business Administration | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 4 | BENG304 | Business Translation | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 5 | BENG305 | International Business Communication | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 6 | BENG306 | English for Logistics | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| Total: | 18 | 270 | 18 | 0 | ||
| Semester 7 (Translation and Interpretation Concentration) | ||||||
| 1 | LING306 | Introduction to Translation and Interpretation | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 2 | TRAN301 | Translation | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 3 | INTE301 | Interpretation | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 4 | LING427 | Contrastive Analysis | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 5 | TRAN401 | Advanced Translation in Practice | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 6 | INTE401 | Advanced Interpretation in Practice | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| Total: | 18 | 270 | 18 | 0 | ||
| Semester 7 (TESOL Concentration) | ||||||
| 1 | LING340 | Theories of English Teaching | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 2 | LING343 | Teaching Activities | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 3 | CALL301 | Computer-Assisted Language Learning | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 4 | ENGL306 | Curriculum Development | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 5 | ENGL307 | Teaching English to Young Learners | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 6 | LING342 | Testing and Assessment | 3 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| Total: | 18 | 270 | 18 | 0 | ||
| Semester 8 | ||||||
| 1. For students whose academic results meet the requirements of the Graduation Thesis | ||||||
| 1 | ENGL396 | Internship | 4 | 120 | 0 | 4 |
| 2 | GRAT396 | Graduation Thesis | 8 | 180 | 4 | 4 |
| Total: | 12 | 300 | 4 | 8 | ||
| 2. For students with different academic results | ||||||
| 1 | ENGL396 | Internship | 4 | 120 | 0 | 4 |
| 2 | GRTE396 | Graduation Essay | 4 | 90 | 2 | 2 |
| 3 | ESP202 | English for Human resources | 2 | 45 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | ENGL401 | English Entrepreneurship | 2 | 45 | 1 | 1 |
| Total: | 12 | 300 | 4 | 8 | ||
| TOTAL CREDITS OF THE TRAINING PROGRAM | 130 | 2070 | 124 | 6 | ||
| Total required credits | 106 | |||||
| Total elective credits | 24 | |||||
